What is Time-Sensitive-Networking (TSN)
Significance of TSN Technology
TSN is an emerging name, but it is not a new technology. It is an IEEE 802.1 TSN task force composed of a series of Ethernet sub-standard definitions and is a technology extending from the field of video and audio data to the field of industry and automobile making. Initially, TSN evolved out of the application need in the audio-video field called "AVB". Audio and video networks that require high bandwidth and high real time can effectively transmit high-quality audio and video with the help of AVB.
In 2006, IEEE 802.1 working group set up AVB Audio and Video Bridging Task Force, aiming at addressing the obstacles of real-time synchronous transmission of data in audio and video networks. Six years later, the AVB Task Force expanded the application requirements and scope of time-deterministic Ethernet in 2012 and was renamed as the TSN Task Force.
As mentioned above, TSN, as a new generation network standard based on Ethernet, has the functions of time synchronization and delay guarantee. In the industrial field, TSN realizes the series connection from the control level to the operation level. TSN is an international standard developed by IEEE, which is more authoritative and will become the first choice for industrial communication in the future.
Overview of IEEE 802.1 Used in TSN
| Standard protocols | Contents |
|---|---|
| IEEE 802.1AS-Rev | Timing and synchronization for time sensitive applications |
| IEEE 802.1Qbu | Frame preemption |
| IEEE 802.1Qbv | Enhancements for scheduled traffic |
| IEEE 802.1Qca | Path control and reservation |
| IEEE 802.1CB | Frame replication and elimination for reliability |
| IEEE 802.1Qcc | Stream reservation protocol enhancements and performance improvements |
| IEEE 802.1Qch | Cyclic queuing and forwarding |
| IEEE 802.1Qci | Pre-stream filtering and policing |
| IEEE 802.1CM | Time-sensitive networking for fronthaul |
| IEEE 802.3br | Interspersing express traffic |
| IEEE802.1Qcr | Bridges and bridged networks amendments: asynchronous traffic shaping |
Integration of OT/IT
The development of intelligent manufacturing, Industrial Internet of Things and big data accelerates the integration of Information Technology (IT) and Operation Technology (OT), and also promotes the increasing demand for a unified network architecture. The different communication needs for IT and OT hinder the integration of these two fields: greater bandwidth is needed for data in the Internet and information fields, while real-time and determinism are the keys for industry. These two kinds of transmission needs are so different that they cannot be met in the same network. As a result, finding a unified solution has become the only way for industrial integration.
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is an industrial communication technology, which is under active promotion in the industry. With TSN, both periodic and aperiodic data can be transmitted
over the same network, giving standard Ethernet the advantage of deterministic transmission. TSN is the way for IT/OT integration, and also the key to accelerate intelligent manufacturing.
Goal and Intention of Industrial Internet of Things
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), as one of the backbone technologies of Industry 4.0, realizes the concept of the Internet of Things in the industrial field, making information technology
and industrial system complement each other. Thanks to the booming IIoT, huge amounts of data are available that make Industry 4.0 and artificial intelligence (AI) possible. Quality
control, green energy-saving and supply chain management see a great prospect. Bain & Company, a management consulting company, forecasts that the output value of the IIoT
will reach $300 billion, twice the value of the consumer IoT.
Current Situations and Perspectives of the IIoT
With the generalization of the IIoT, persisting efforts will be made for digitalization, automation and innovation in the industry, and the variability of application cases and scenarios will be promoted. A large number of devices will produce huge amount of data and promote the closer connection among machine, device and people. These OT-side devices are expected to improve business performance, employee efficiency, and customer satisfaction through improved efficiency, flexibility and availability over a more reliable and highly scalable network.
Difficulties in the Integration of OT/IT
1. Complex Fieldbus of OT itself
Fieldbus has different characteristics in physical medium, node number, transmission distance, bandwidth and transmission
capacity. Therefore, in the implementation of the IIoT, data communication between devices requires a large number of Fieldbus and protocol conversion devices at a huge cost.
This poses a huge challenge to intelligent manufacturing, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises.
2. The different data characteristics between IT and OT contribute to the difference in network needs
OT represents the Operation Technology, covering the operation and process control of the Industrial Control System (ICS). For the construction of industrial automation network, the system usage convention of OT environment is stability overweight innovation, which puts forward the requirements of real-time, reliability and integrity. The ever-changing IT network technology and network security are less attractive for the OT environment. IT refers to the Information Technology. Unlike OT, which focuses on real-time reliability, IT prefers confidentiality, integrity and availability, so it is more common to see IT technicians applying new technologies. In the operation context of the IIoT, such widely divergent user habits and system environment architecture gradually collide, and the challenges encountered in the integration of technology and concept are as great as expected.
3. Difference in real-time
As mentioned above, different OT/IT needs lead to different expectations for the network. The microsecond OT control tasks must be completed by using the network with a very low latency and jitter. IT pays more attention to data load and information security, putting less demand for real-time. The real implementation of the IIoT requires actively looking for solutions that can satisfy both OT and IT.
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) Shines Through the Hazy Future
TSN is a series of IEEE 802.1 TSN task forces composed of the Ethernet sub-standard definitions, namely a group of "sub-standards" under IEEE 802.1 standard, aiming to establish a time-sensitive mechanism for Ethernet protocol, so as to ensure that all network data transmissions are conducted in the same architecture and guarantee the time determinism. The primary challenge in getting different protocols to run on the same infrastructure is configuring critical and non-critical data flows that do not affect either real-time or performance.
From a simple level, TSN is a technology to control the communication bandwidth based on the setting of the priority of communication frames by using the time division method of Ethernet communication bandwidth, which enhances the determinism and reliability of the standard Ethernet, and enables Ethernet to provide both stable and consistent transmission services for critical data. Extensions and adjustments to the existing Ethernet standards address the differences in the transmission property of OT periodic data and IT aperiodic data. The requirements of real-time for OT and large data capacity and many nodes for IT are both met, which enables the integration of Information Technology (IT) and industrial Operation Technology (OT) to be realized.
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) Has Advantages over Traditional Ethernet for Several Reasons:
1. Ensure accurate and stable delay time for critical real-time data across the network
2. Capable of simultaneously transmitting critical and non-critical data flows
3. High-level protocol layers can share network infrastructure
4. Real-time control is also possible beyond the Operation Technology (OT) field
5. Easier integration of subsystems
6. Components can be added without changing the network or device
7. More efficient diagnosis and repair of network faults
Move the slider to see what happens
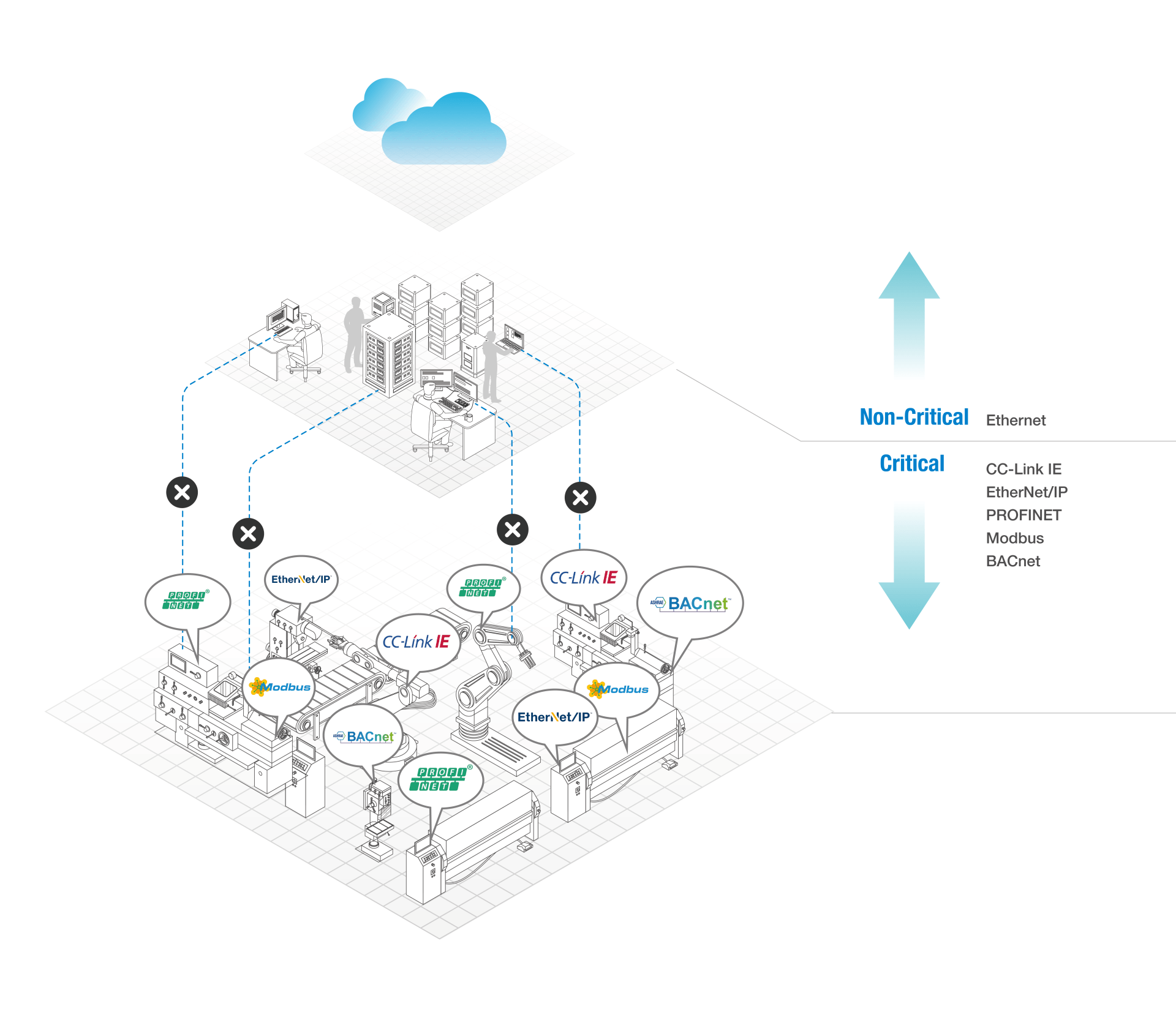
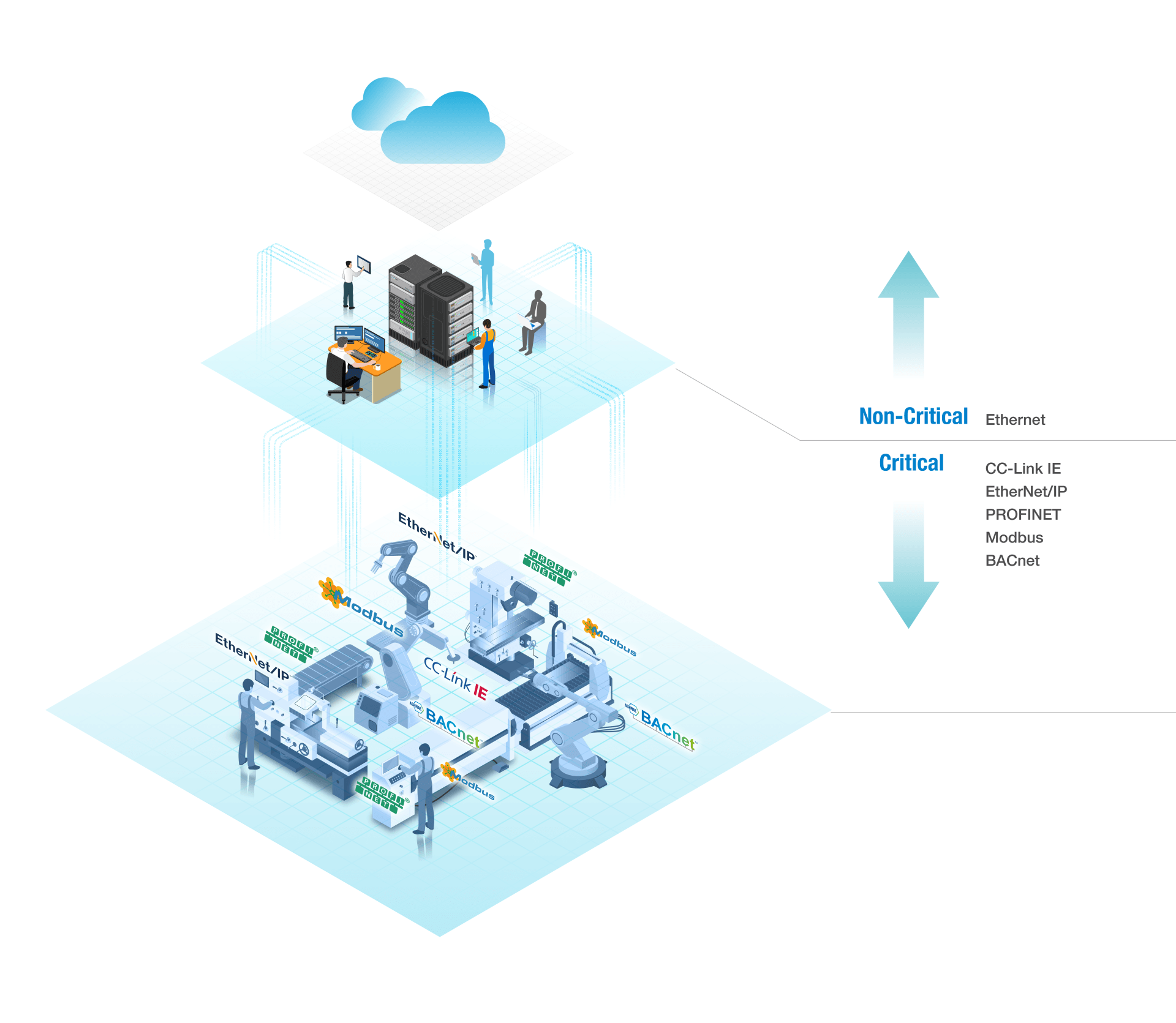
Actual Benefits of TSN to Users
1
With TSN, devices can communicate in real time without barriers, simplifying the configuration of systems, devices and applications, and increasing productivity by enabling machines to run together rather than independently. The vision of the IIoT is to achieve smooth communication between things, to integrate devices with the needs of the network, and to facilitate big data analysis and cloud management. The IIoT also provides a lot of support for machine learning and artificial intelligence.
2
The standardization technology carried out by TSN enables the structure to be standardized and flexibly extended without worrying about compatibility issues, thus resulting in higher flexibility. Previously different infrastructure technologies, protocols, and topologies are a stumbling block to network configuration. Standardized management of different modules and extension units can improve construction efficiency and reduce maintenance time, manpower and money costs.
3
TSN increases the amount of data available
and enables true real-time monitoring of production, eliminating the need for data collection, uploading and reporting at fixed time points. The performance indicators composed of the data are more accurate, detailed and real-time, conductive to a more complete and high-quality operation management.
4
TSN enables the devices on the production
site to successfully connect with the Ethernet and related infrastructure to obtain more network application services, including computing, classification, quality control, and image monitoring.
Application Field of TSN
TSN is a standard certified by industry organizations. A large number of organizations and enterprises at home and abroad are actively promoting the development of TSN technology and conducting interoperability testing, so as to jointly transform the ideal concept of the IIoT into practice. TSN consists of a number of IEEE standards, some of which are under development, and some of which are already widely applied by practitioners in the industry. From this, it can be inferred which fields are more suitable for the active deployment of TSN environment:
Advantech Time-Sensitive Networking Product Offerings
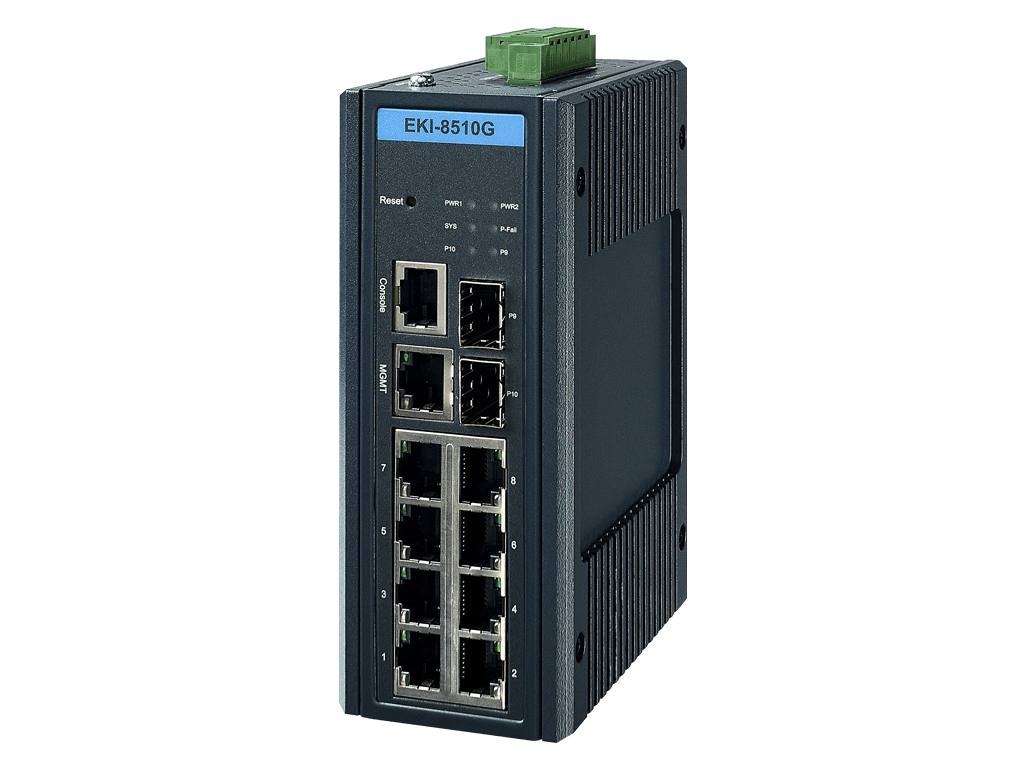
Industrial Managed TSN Switch
EKI-8510
The EKI-8510G-2FI is the next generation of industrial switch which supports real-time communication through Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) technology. Providing a means for determinism over Ethernet-based networks and guarantee the delivery for those critical real-time applications.
- 8 x Gigabit ports + 2 x Gigabit SFP ports
- IEEE 1588v2 PTP Precision Time Protocol
- Features IEEE 802.1AS Time Synchronization, IEEE 802.1Qbu Frame Preemption, IEEE 802.1Qbv Time Aware Shaper and IEEE 802.1CB Seamless Redundancy
- SFP socket for easy and flexible fiber expansion
- Management: SNMP v1/v2c/v3, WEB, Telnet, standard MIB
- NEMA TS2 for traffic control and EN 50121-4 approval for railway track sides
- Dual 12~48 VDC power input and 1 x relay output
Industrial TSN DIN-Rail Controller
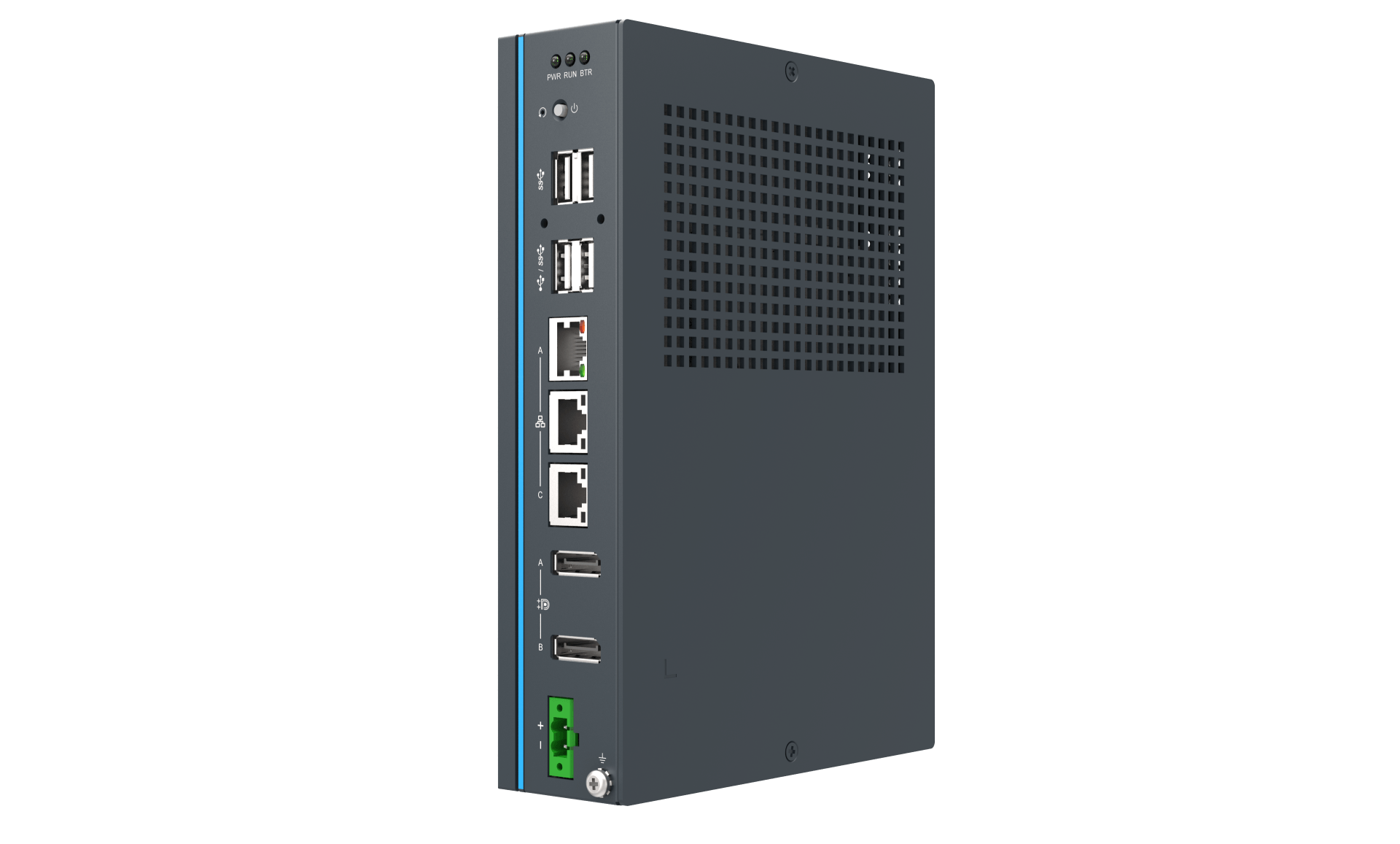
UNO-148
UNO-148 is a new generation DIN-Rail Controller equipped with newest 11th Generation Intel® Core™ i Processor (up to 4.4GHz), supporting new solutions require high degree of coordination networked equipment. Also, UNO-148 can provide extra reliable and low latency communication requirement from eal-time application.
- 11th Generation Intel® Core™ i Processor with most 32GBx2 DDR4 memory (Default 8GB)
- IEEE 1588(PTPv2) enhances the accuracy of time synchronization
- IEEE 802.1AS(gPTP) featured best master clock selection, path delay measurement, and time distribution
- IEEE 802.1Qbv guarantee low transmission latency and timely delivery
- Support M.2 2280 NVMe SSD
- Modular design for optional iDoor extension
- Compliant with IEC 61010-1 safety requirements
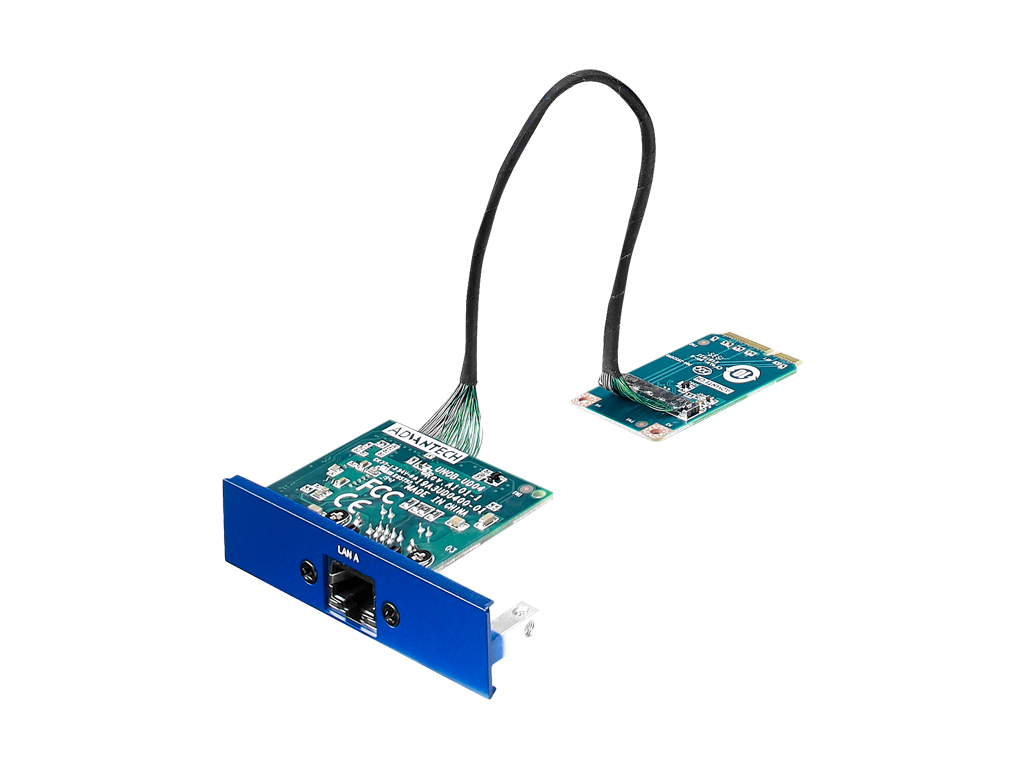
Industrial TSN iDoor Module
PCM-24R1TP-BE
PCM-24R1TP-BE is the mPCIe extension module designed to address the needs of control systems with standard Ethernet technology, including standard time synchronization and deterministic network communication over standard Ethernet which allows operations networks to leverage the advantages of traditional Ethernet while meeting the timing and control needs of control and measurement applications.
- Supports Time Sensitive Network (TSN) (IEEE 1588/ 802.AS Rev, 802.1Qav, 802.1Qbv)
- Support PXE
- High speed Ethernet supports 10BASE-Te, 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T and 2500BASE-T 802.3
- Achieves time synchronization for device or system
- Real-time Ethernet with hardware based precision time protocol
Frequently Asked TSN Questions
Standard protocols
Device management and network security
Technology and operation details
Advantech Newsletter
Sign up for the latest intelligent connectivity product and event updates,
industry news, case studies, and more from Advantech.
Follow Advantech